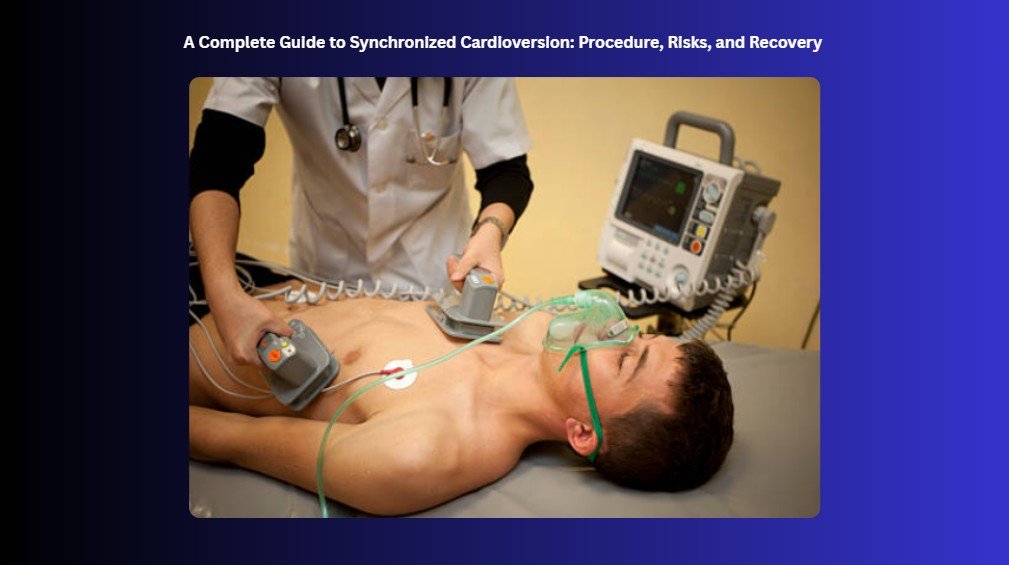
Synchronized cardioversion is a medical procedure used to restore a normal heartbeat in people with irregular or rapid heart rhythms. During the process, a small electrical shock is delivered at the precise moment in the heartbeat cycle, timed to the heart’s electrical activity to safely reset its rhythm. Accurate ECG rhythm recognition and interpretation, especially in ACLS, play a critical role in determining when and how the shock should be delivered. Usually performed quickly in a hospital or emergency setting, this safe and effective procedure can help your heart beat normally again.
Many people think cardioversion and an AED (automated external defibrillator) are the same, but they are different. Cardioversion is a medical procedure done by doctors to fix certain heart rhythm problems using a controlled electric shock. On the other hand, an AED is a device anyone can use during emergencies to help restart a heart that has stopped beating. So while both use electricity to help the heart, one is planned and done by professionals, and the other is for sudden emergencies, which anyone can act on.
In this guide, we’ll explain the cardioversion procedure, possible risks, and what to expect during recovery. This common treatment can significantly improve how you feel.
What does cardioversion treat?
Cardioversion is a procedure that restores a normal heart rhythm when your heartbeat is irregular or too fast, helping to ease symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and dizziness. It is commonly used to manage several heart rhythm disorders.
1. Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter: These conditions cause the upper chambers of the heart to beat erratically. Cardioversion delivers a gentle electrical shock to reset the heart’s rhythm, improving how you feel and lowering the risk of heart-related complications.
2. Atrial Tachycardia: In this condition, the heart’s upper chambers beat rapidly. Cardioversion can slow the heartbeat and re-establish a steady rhythm, easing discomfort and reducing concerns about the accelerated rate.
3. Ventricular Tachycardia: Here, the lower chambers experience a dangerously fast rhythm. Cardioversion stops the rapid heartbeat, helping to prevent severe problems and stabilize your condition quickly.
4. Ventricular Fibrillation: This is a life-threatening emergency where the heart quivers instead of pumping blood effectively. Cardioversion provides an urgent electrical shock to restore an effective heartbeat and save your life.
Types of Synchronized Cardioversion
Doctors use two main methods of synchronized cardioversion to treat irregular heart rhythms. One method delivers an electrical shock, while the other relies on medications to restore a steady heartbeat.
1. Electrical Cardioversion
The electrical cardioversion procedure delivers a controlled, gentle electric shock to your heart through patches placed on your chest. The shock aims to reset your heart’s electrical activity and promote a regular heartbeat. Many patients experience quick relief and improvement shortly after the treatment.
2. Chemical Cardioversion (Pharmacological)
Chemical cardioversion involves using specific medications to return your heart to a stable rhythm. These drugs can be administered intravenously or taken orally to regulate or normalize your heartbeat. This option is often preferred by those who want to avoid electrical shocks and can be quite effective as well.
Procedure of Synchronized Cardioversion
Synchronized cardioversion is a carefully planned process that helps your heart beat normally again using electricity or medicine. It involves preparing your body, delivering the treatment, and then watching your recovery to make sure everything stays on track.
1. Preparation
Before starting the procedure, the doctor checks your health to make sure you’re ready and comfortable. They give you medication to help you relax and place small patches called electrodes on your chest. Then they set up the defibrillator to prepare for delivering a gentle shock if needed.
2. Procedure
During the procedure, the doctor chooses the right amount of energy for the shock and then charges the machine. They make sure no one is touching you before delivering the shock to keep everyone safe. After the shock, they closely monitor your heart to see how it responds and ensure it returns to a normal rhythm.
3. Post-Procedure
After the procedure, you will rest for a little while while your heart gets back to normal. The doctor might adjust your medications to help keep your heartbeat steady and healthy. They will also schedule follow-up visits to check on your progress and ensure everything is still on track for good heart health.
Advantages of Cardioversion
Cardioversion can quickly restore your heart’s normal rhythm, easing symptoms like palpitations or dizziness and improving overall heart function. This safe and effective treatment often leads to better energy levels, a more active lifestyle, and sometimes reduces the need for long-term medications.
- Rapid Symptom Relief: Cardioversion provides fast relief from uncomfortable symptoms caused by an irregular heartbeat. Many patients notice improvements soon after the procedure, helping them feel better and more comfortable in daily life.
- Improve Heart Functions: By restoring a regular heartbeat, cardioversion allows your heart to pump blood more efficiently, supporting the health of your organs and boosting your energy.
- Safe and Effective: Performed by skilled medical professionals, cardioversion has a high success rate with minimal risks, making it a reliable treatment for irregular heart rhythms.
- Reduced Reliance on Long-Term Medicines: Restoring normal heart rhythm can decrease the reliance on daily medications, simplifying treatment and reducing potential side effects.
- Reduced Risk of Stroke: A regular heartbeat helps prevent blood clots, reducing the chance of stroke and protecting your long-term health. It’s also crucial to recognize signs of impending death after a stroke so you can seek immediate help if needed and take steps to protect your well-being.
Risks and Potential Complications of Cardioversion
Having a cardioversion procedure always comes with some risks, but understanding them can help you feel more prepared. Let’s look at some common and less common complications that might happen.
1. Common Risks
Many people face these common risks after the cardioversion, but knowing about them can help you stay informed and calm.
1a. Reoccurrence of Arrhythmias: One common risk is that the irregular heartbeat might come back even after treatment. It’s important to keep up with follow-ups so your doctor can catch any changes early.
1b. Blood Clots: Another possible risk is the formation of blood clots, which can travel and cause serious problems like a stroke. Your doctor may suggest blood thinners to help lower this risk.
1c. Irritation or Skin Burn: Sometimes, the treatment can cause mild skin irritation or a small burn where the pads were placed. This usually heals quickly and isn’t something to worry too much about.
2. Less Common Risks
In rare cases, the heart might not pump as well, get slightly damaged, or take a little time to work normally again after treatment.
2a. Heart Failure: In some rare cases, the heart may become weaker and struggle to pump blood as it should. Your care team will watch closely for any signs and help manage them right away.
2b. Heart Damage: There’s a small chance the heart muscle could get slightly injured during the procedure. Doctors take special care to avoid this and will check how your heart is doing afterward.
2c. Atrial Stunning: Sometimes after treatment, the upper part of the heart might not start working normally right away. This usually gets better on its own with a little time and rest.
Tips for Safe Recovery after Cardioversion
Here are some helpful tips to make sure your recovery after cardioversion goes smoothly.
- Rest and Take It Easy: Give your body time to heal by avoiding heavy activities for a few days.
- Follow Your Doctor’s Advice: Take all medications as prescribed and go to all follow-up appointments.
- Watch for Any Symptoms: If you notice chest pain, shortness of breath, or feeling dizzy, contact your doctor right away.
- Keep Your Skin Clean and Dry: Gently care for the area where the pads were placed to prevent irritation.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Well: Drinking plenty of water and eating balanced meals can help your body recover faster.
Navigating Synchronized Cardioversion Safely and Effectively
In summary, synchronized cardioversion is a safe, often quick way to restore your heart to a steady rhythm. While the idea of an electrical shock might sound scary, the procedure is performed carefully by skilled professionals who prioritize your safety and comfort. Most people feel much better afterward, with fewer symptoms and more energy. Understanding the heart’s electrical activity, as covered in Understanding the PQRST Wave: A Guide to ECG Interpretation, can also help you appreciate how cardioversion resets your heart’s rhythm. Of course, it’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and monitor how you’re feeling as you recover. With proper care and rest, many find that cardioversion helps them get back to their normal life faster and with greater peace of mind. If you ever have questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare team; they’re there to support you every step of the way.
Stay ready to save a life with Bayside CPR. Our streamlined training combines a short online course with a 30-minute in-person skills session at over 60 locations, making certification fast and convenient. Earn your AHA Standard ACLS, BLS, PALS, CPR, or First Aid certification and receive your official card the same day, so you’re prepared to act.