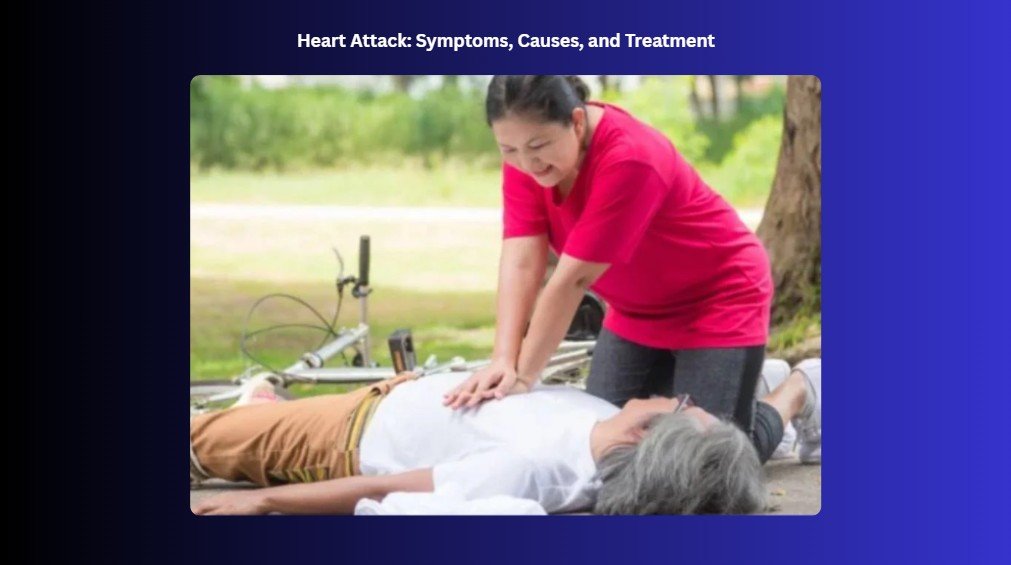
It’s terrifying to see someone suddenly clutch their chest, their face paling, struggle for breath. They double over, frowning in pain, and then, suddenly, everything changes to silence. You realize they might be having a heart attack. Your heart races, but you know what to do. Every second matters. Calling emergency services, keeping them calm, and helping them sit or lie down, these simple actions can make all the difference. Heart attacks are serious; it is also known as myocardial infarction in medical terms. It happens when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked. This blockage typically occurs in the coronary artery, which supplies blood to the heart. But with quick action, you could be their lifeline, giving them a chance to survive when every moment counts.
According to the AHA, about every 40 seconds, someone in America has a heart attack. If a large part of the heart muscle is damaged during a heart attack, the heart may no longer be able to pump blood efficiently, leading to heart failure. This can cause fluid buildup, shortness of breath, and fatigue. A heart attack can also lead to cardiac arrest if the damage to the heart muscle disrupts the heart’s electrical system, causing it to stop beating effectively.
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) does not treat a heart attack, but it becomes crucial if a heart attack leads to cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating, and CPR can help circulate blood to the brain and other vital organs until professional help arrives. It can significantly increase a person’s possibilities of survival in such situations. Immediate medical treatment, like medications or surgery, is necessary to address the underlying blockage. There are two kinds of CPR. They are: Hands-Only CPR and Traditional CPR.
What Are the Symptoms of a Heart Attack?
Not everyone will experience a heart attack in the same way. Some people have different symptoms. Here are some symptoms of it :
- Chest Discomfort: Imagine a heavy weight pressing on your chest or a squeezing sensation that doesn’t go away. This feeling, often centered in the chest, might last for a few minutes or come and go.
- Pain Spread: This isn’t your average muscle ache. The discomfort might spread to your shoulders, neck, arms, or even your jaw.
- Worsening Chest Pain: If the chest pain intensifies rather than subsides, it’s a red flag.
- Persistent Pain: Resting or taking heart medications doesn’t ease the chest pain? That’s a concern.
- Additional Symptoms: Sometimes, the chest pain is accompanied by nausea, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, or cold sweats.
Also, Read: How Technology Is Transforming Heart Monitoring
What Causes Heart Attack?
When arteries get clogged with plaque, it can block blood flow to the heart, triggering a heart attack. The main causes include:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): Build-up of fatty plaques (atherosclerosis) inside the coronary arteries.
- Plaque rupture: A plaque can rupture, causing a blood clot to form and block the artery.
- Blood clots: These can form on top of unstable plaques or due to other conditions.
- Coronary artery spasm: Temporary narrowing of the arteries, possibly triggered by drugs, cold, stress, or smoking.
- Other factors: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, inactivity, stress, and family history.
Are Heart Attack Genetic?
Your family history plays a role in determining your chances of developing heart disease. Here is a breakdown of it :
- If your parent or sibling had a heart attack or struggled with conditions like high blood pressure or high cholesterol, your own risk goes up.
- Some heart problems, like familial hypercholesterolemia, are directly passed down through your genes.
- Heart disease isn’t usually caused by just one gene, but a mix of genetic factors can make you more likely to develop it.
- Lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and smoking also play a crucial role in heart disease prevention and can influence how genes affect risk, according to Penn Medicine.
- Mass General Brigham lists inherited heart conditions like Long QT syndrome and Marfan syndrome, which can increase the risk of heart-related problems.
How to Prevent Heart Attacks?
To prevent the risk of heart attack, adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes eating a nutritious diet, staying physically active, avoiding tobacco use, and controlling your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar within healthy ranges. Here are the seven ways to reduce the chance of a heart attack:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet – Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (like olive oil and nuts). Limit salt, sugar, and saturated fats.
- Exercise regularly – Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week (like brisk walking or cycling).
- Quit smoking – Smoking damages blood vessels and significantly increases heart disease risk.
- Manage stress – Use stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or therapy to lower blood pressure and heart strain.
- Maintain a healthy weight – Excess weight, especially around the waist, increases the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Control blood pressure – Monitor your blood pressure and follow your doctor’s advice for keeping it within a healthy range.
- Manage cholesterol levels – Keep LDL (bad) cholesterol low and HDL (good) cholesterol high through diet, exercise, and medication if prescribed. Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider help monitor heart health, manage risk factors, and detect issues early to prevent heart attacks.
- Visit doctor: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider help monitor heart health, manage risk factors, and detect issues early to prevent heart attacks.
Types of Heart Attack
A healthy heart maintains a regular heartbeat and ensures normal blood flow throughout the body by pumping oxygen-rich blood through its chambers and arteries. When this normal rhythm or circulation is disrupted, it can result in a heart attack. There are several types of heart attacks, each caused by different blockages or irregularities in blood flow:
- STEMI (ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction): This is the most serious type of heart attack. It happens when a major artery is completely blocked, cutting off blood to a large part of the heart. People often feel intense chest pain, and immediate emergency treatment is critical.
- NSTEMI (Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction): In this type, the artery is only partially blocked, so the damage to the heart may be less severe, but it’s still scary. Symptoms might feel milder, but it still requires urgent care and close monitoring.
- Silent Heart Attack: This one is tricky because it doesn’t cause the classic symptoms like crushing chest pain. Some people may just feel tired, short of breath, or a bit off, and they may not even realize they had a heart attack until a doctor finds signs of heart damage later on.
- Coronary Artery Spasm (Prinzmetal’s Angina): This type doesn’t always come from a blockage. Instead, the artery suddenly tightens or spasms, briefly reducing blood flow to the heart. It can happen at rest, often during the night or early morning, and the chest pain can feel intense even though there’s no physical blockage.
How Long Do Heart Attacks Last?
A heart attack can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. Here’s a breakdown to help clarify:
- It can be minutes or hours. Some people might feel symptoms for just a few minutes, while others experience discomfort that drags on longer.
- Often, the most intense symptoms last around 20-30 minutes, like crushing chest pain, shortness of breath, or cold sweats.
- Sometimes, warning signs come and go. Feeling a bit off, then better, then worse again, which can make it tricky to recognize as a heart attack.
- Delayed treatment makes it worse. The longer the blockage stays, the more damage your heart can sustain.
- In severe cases, the damage can be ongoing. If not treated quickly, symptoms might last longer and cause significant heart muscle damage.
Note: Remember, if you or someone else ever suspects a heart attack, seek emergency help immediately. Early intervention can save lives!
Is It Possible to Have Two Heart Attacks in One Day?
Experiencing two heart attack in one day is very serious and rare, but unfortunately, it can happen. Here’s what that involves:
- It indicates ongoing severe blockage or damage; the heart continues to be under stress after the first attack, causing a second one.
- It’s a medical emergency; immediate treatment is crucial to prevent further damage or death.
- It often happens when the initial attack isn’t fully treated or the underlying problem isn’t managed, like ongoing artery blockage or blood clots forming again.
- Recovery can be complicated. The heart might suffer more damage, and the person may need intensive care, medications, or surgery.
- The chances of complications are higher. Double attacks can increase the risk of heart failure or other issues.
Note: If someone exhibits signs of a second attack after the first, it’s critical to call emergency services right away. Prompt action can make all the difference.
Stay Prepared and Act Fast: Your Heart Health Is in Your Hands
In summary, recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack and taking quick action can truly save a life. Whether you’re experiencing chest pain, discomfort spreading to other areas, or unusual signs like nausea or cold sweat, don’t hesitate, call 911 emergency services immediately. Living a heart-healthy lifestyle by eating well, exercising, managing stress, avoiding risk factors, and understanding the most common heart medications can make a big difference. Remember, rapid response isn’t just crucial, it’s lifesaving. We train you to respond confidently to emergencies like suspected stroke, heart attack, cardiac arrest, bradycardia, tachycardia, and more for infants, children, and adults.
Register now at Bayside CPR and become a life-saving hero! Choose from BLS, ACLS, PALS, CPR, or First Aid courses. This training is suitable for medical professionals, sports coaches, parents, teachers, and other healthcare providers. Start with a short online class, then attend a 30-minute in-person skills session at one of our 60+ locations. You’ll gain hands-on practice and essential knowledge, including how to properly use an AED. Leave the same day with your official AHA Standard certification card, confident and prepared to respond in an emergency.